At the heart of financial accounting is the system known as double-entry bookkeeping (or “double entry accounting”). Each financial transaction that a company makes is recorded by using this system. Technology enhances accounting by automating processes, improving accuracy, and providing real-time insights. Understanding how tools like AI and cloud-based software streamline workflows and reduce errors reflects adaptability and integration into traditional practices.
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
This involves strategic thinking and adaptability, balancing competing priorities without compromising financial integrity. Budget forecasting requires analytical skills, strategic thinking, and an understanding of financial landscapes. Integrating data points, anticipating trends, and aligning forecasts with organizational goals are key. This process involves synthesizing complex data into actionable insights, guiding decision-making and resource allocation. To demonstrate the skills necessary for excelling in an accounting role, candidates should provide concrete examples from their past experiences that highlight their competencies.
Financial Statements
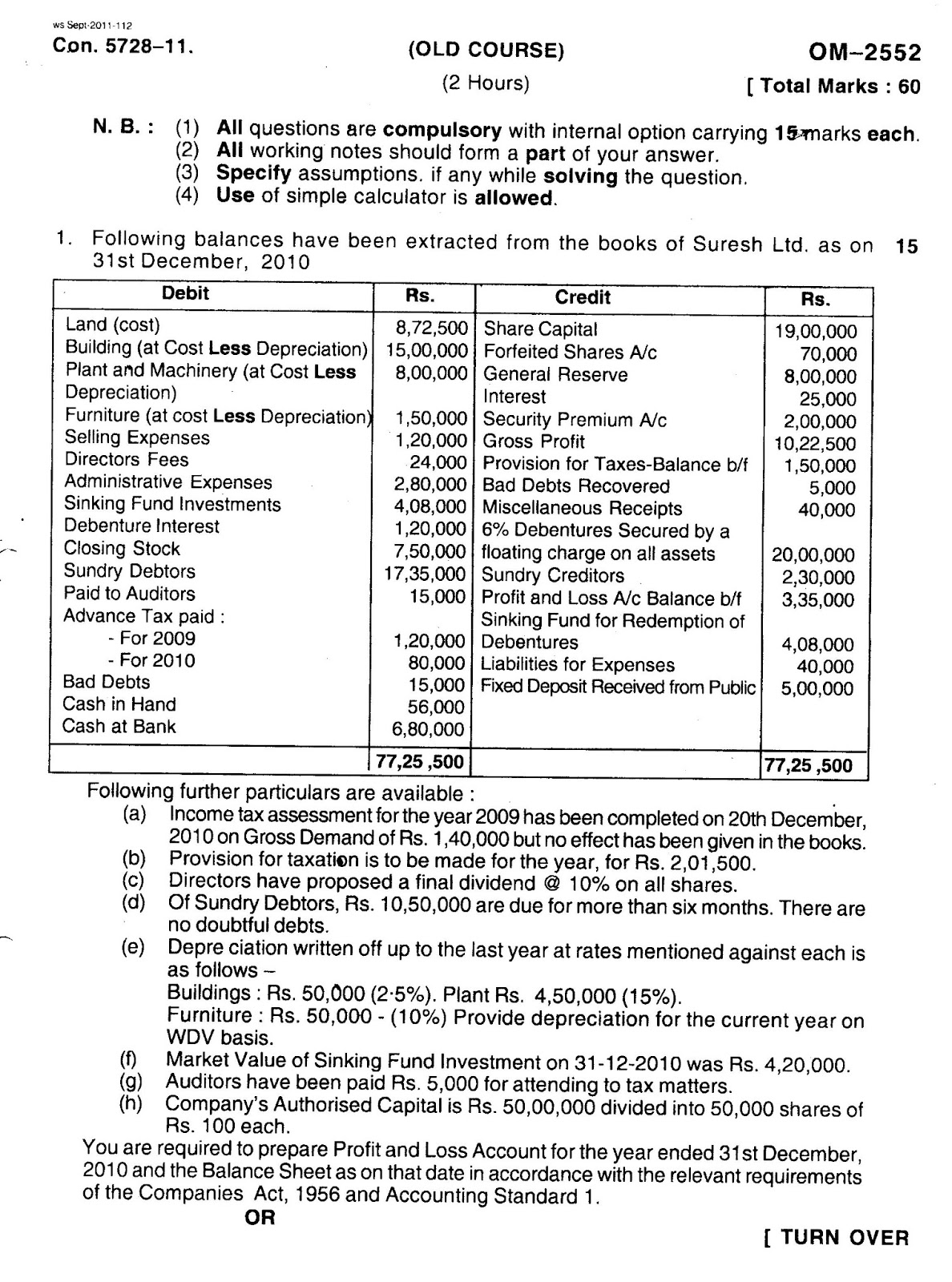
The key difference between financial and managerial accounting is that financial accounting provides information to external parties, while managerial accounting helps managers within the organization make decisions. Even though the company won’t pay the bill until August, accrual accounting calls for the company to record the transaction in July, debiting utility expenses. A shareholders’ equity statement reports how a company’s equity changes from one period to another, as opposed to a balance sheet, which is a snapshot of equity at a single point in time. A cash flow statement is used by management to better understand how cash is being spent and received. It extracts only items that impact cash, allowing for the clearest possible picture of how money is being used, which can be somewhat cloudy if the business is using accrual accounting. Financial accounting rules regarding an income statement are more useful for investors seeking to gauge a company’s profitability and external parties looking to assess the risk or consistency of operations.
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
Usually issued on a monthly, quarterly, or annual basis, the income statement lists the revenue, expenses, and net income of a company for a given period. Financial accounting guidance dictates how a company recognizes revenue, records expenses, and classifies types of expenses. U.S. public companies are required to perform financial accounting in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). Their purpose is to provide consistent information to investors, creditors, regulators, and tax authorities. This information can come from Financial Statements, internal reports, surveys, and other sources. By analyzing this data, accountants can make informed decisions to help the company achieve its goals.
Financial Accounting Meaning, Principles, and Why It Matters
When the company earns the revenue next month, it clears the unearned revenue credit and records actual revenue, erasing the debt to cash. Financial accounting guidance dictates when transactions are to be recorded, though there is often little to no flexibility in the amount of cash to be reported per transaction. Work opportunities for a financial accountant can be found in both the public and private sectors.
- It’s a chance to showcase your knack for detail, your problem-solving prowess, and your passion for precision.
- International public companies also frequently report financial statements in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
- Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible.
- Financial accounting is a specific branch of accounting involving a process of recording, summarizing, and reporting the myriad of transactions resulting from business operations over a period of time.
Navigating the world of accounting interviews can feel a bit like balancing a checkbook—precise, sometimes challenging, but ultimately rewarding. As an accountant, you’re not just crunching numbers; you’re the financial backbone of any organization. Interviewers know this and will ask questions designed to assess not only your technical skills but also your ability to irs issues 2021 mileage rates for business, medical, charity travel communicate complex financial concepts with clarity and confidence. It’s a chance to showcase your knack for detail, your problem-solving prowess, and your passion for precision. Members of financial accounting can carry several different professional designations. The transaction is recorded as a debit to cash and a credit to unearned revenue, a liability account.
These transactions are summarized in the preparation of financial statements—including the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement—that record a company’s operating performance over a specified period. Revenues and expenses are accounted for and reported on the income statement, resulting in the determination of net income at the bottom of the statement. Assets, liabilities, and equity accounts are reported on the balance sheet, which utilizes financial accounting to report ownership of the company’s future economic benefits.
Understanding the difference between cash and accrual accounting is essential for accurately capturing a business’s financial state. Cash accounting recognizes revenue and expenses when money changes hands, offering a straightforward view of cash flow. Accrual accounting records income and expenses when they are earned or incurred, providing a comprehensive picture of a company’s financial position over time.
It lists the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity, and the financial statement rolls over from one period to the next. Financial accounting guidance dictates how a company records cash, values assets, and reports debt. Financial accounting is a branch of accounting that focuses on the recording, summarizing, and reporting of a company’s financial transactions and activities. Its primary purpose is to provide relevant and reliable financial information to external stakeholders, such as investors, creditors, regulators, and the general public.
The annual report to the SEC requires that independent certified public accountants audit a company’s financial statements, thus giving assurance that the company has followed GAAP. Financial accounting is required to follow the accrual basis of accounting (as opposed to the “cash basis” of accounting). Under the accrual basis, revenues are reported when they are earned, not when the money is received. For example, although a magazine publisher receives a $24 check from a customer for an annual subscription, the publisher reports as revenue a monthly amount of $2 (one-twelfth of the annual subscription amount).









